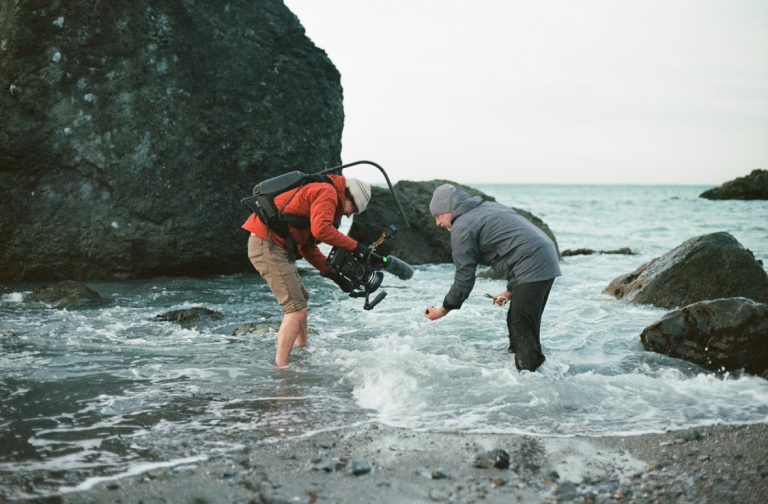
What Are the Different Jobs in the Film Industry and TV?
When I moved to Los Angeles in 2012, I had no idea how much this city ran on the jibs Hollywood provided. The thing is, we often hear about writers, directors, and actors, but the film and television industry provides thousands of other jobs to people. Those may be jobs you never heard about or dreamt about, but they can provide great and long careers. So, today, I wanted to take you through some of the jobs in the film industry.Let's dive in. Film Industry Job Glossary A Above-the-Line: Key creative personnel like the director, writer, producer, and principal actors. Their salaries are negotiated as a percentage of the film's budget. Actor: Portrays characters in a film. ADR (Automated Dialogue Replacement) Editor: Manages the process of re-recording dialogue in a studio. Agent: Represent screenwriters, directors, and other creatives, negotiate deals, and manage their careers. Animal Wrangler: Cares for and trains animals used in film and TV. Archivist: Preserves and restores film and TV. Armorer: Responsible for the safety and maintenance of firearms on set. Art Director: Oversees the visual look of the film's sets and locations, and works closely with the production designer. Assistant Director (AD): Manages the on-set logistics and schedules. There are often multiple ADs (1st AD, 2nd AD, etc.) with varying levels of responsibility. Associate Producer: A production role with different responsibilities, often assists the producer on specific tasks. Audio Engineer: Record, mix, and master sound during production and post-production. B Best Boy: The gaffer's (lighting) or key grip's (rigging) right-hand person. Boom Operator: Holds the boom pole, which carries the microphone, during filming to capture sound. C Carpenter: Builds and repairs sets. Casting Director: Finds and auditions actors for the various roles in a film. Cinematographer (Director of Photography - DP): Responsible for the visual look of the film, including lights, camera angles, and film stock, or digital format. Closed Captioning/Subtitling: Creates subtitles and closed captions for films. Colorist: Adjusts the colors in the film to create a specific look and mood. Composer: Writes the film's score. Costume Designer: Creates the costumes for the actors, based on the characters and the film's overall style. Craft Service: Provides food and drinks for the cast and crew on set. Creative Producer: A producer involved in the creative development of the film. D Development Executive: Works for a production company or studio, and finds and develops scripts and projects. Dialogue Editor: Cleans up and synchronizes dialogue records. Director: The creative head of the film, responsible for overseeing all aspects of the production, from pre-production to post-production. Director of Photography (DP): See Cinematographer. Distributor: The company responsible for releasing the film to theaters and other platforms. Documentary Filmmaker: Creates non-fiction films, often focusing on real-life events and people. Dolly Grip: Operates the dolly, a wheeled platform used to move the camera. E Editor: Assembles the raw footage into the final film, and creates the narrative flow and pacing. Electrician: Works with the gaffer to set up and maintain lighting equipment. Executive Producer: Often involved in financing and high-level decision-making, but may not be involved in the day-to-day production. F Film Critic: Reviews and analyzes films. Film Festival Programmer: Select films to be screened at film festivals. Focus Puller: Maintains the camera's focus during filming. Foley Artist: Creates and records everyday sound effects for films in post-production. G Gaffer: The head electrician on set, responsible for executing the lighting plan designed by the cinematographer. Grip: Responsible for the rigging and support of camera equipment, as well as other on-set tasks. H Hair Stylist: Styles the actors' hair for filming. K Key Grip: The head grip on set, responsible for overseeing the grip crew. L Line Producer: Manages the budget and logistics of a film production. Location Manager: Finds and secures locations for filming. M Marketing Manager: Develops and executes the marketing campaign for the film. Makeup Artist: Applies makeup to the actors for filming. Music Supervisor: Selects and licenses music for the film. P Post-Production Supervisor: Oversees the post-production process, ensures that the film is completed on time and within budget. Producer: Oversees the entire film production, from development to distribution. There are various types of producers with different responsibilities. Production Assistant (PA): Entry-level position that covers various tasks on set, from running errands to assisting the crew. Production Designer: Creates the overall visual look of the film, including sets, costumes, and props. Prop Master: Responsible for acquiring and managing all props used in the film. Publicist: Promotes the film to the media and the public. S Sales Agent


When I moved to Los Angeles in 2012, I had no idea how much this city ran on the jibs Hollywood provided. The thing is, we often hear about writers, directors, and actors, but the film and television industry provides thousands of other jobs to people.
Those may be jobs you never heard about or dreamt about, but they can provide great and long careers.
So, today, I wanted to take you through some of the jobs in the film industry.
Let's dive in.
Film Industry Job Glossary
A
- Above-the-Line: Key creative personnel like the director, writer, producer, and principal actors. Their salaries are negotiated as a percentage of the film's budget.
- Actor: Portrays characters in a film.
- ADR (Automated Dialogue Replacement) Editor: Manages the process of re-recording dialogue in a studio.
- Agent: Represent screenwriters, directors, and other creatives, negotiate deals, and manage their careers.
- Animal Wrangler: Cares for and trains animals used in film and TV.
- Archivist: Preserves and restores film and TV.
- Armorer: Responsible for the safety and maintenance of firearms on set.
- Art Director: Oversees the visual look of the film's sets and locations, and works closely with the production designer.
- Assistant Director (AD): Manages the on-set logistics and schedules. There are often multiple ADs (1st AD, 2nd AD, etc.) with varying levels of responsibility.
- Associate Producer: A production role with different responsibilities, often assists the producer on specific tasks.
- Audio Engineer: Record, mix, and master sound during production and post-production.
B
- Best Boy: The gaffer's (lighting) or key grip's (rigging) right-hand person.
- Boom Operator: Holds the boom pole, which carries the microphone, during filming to capture sound.
C
- Carpenter: Builds and repairs sets.
- Casting Director: Finds and auditions actors for the various roles in a film.
- Cinematographer (Director of Photography - DP): Responsible for the visual look of the film, including lights, camera angles, and film stock, or digital format.
- Closed Captioning/Subtitling: Creates subtitles and closed captions for films.
- Colorist: Adjusts the colors in the film to create a specific look and mood.
- Composer: Writes the film's score.
- Costume Designer: Creates the costumes for the actors, based on the characters and the film's overall style.
- Craft Service: Provides food and drinks for the cast and crew on set.
- Creative Producer: A producer involved in the creative development of the film.
D
- Development Executive: Works for a production company or studio, and finds and develops scripts and projects.
- Dialogue Editor: Cleans up and synchronizes dialogue records.
- Director: The creative head of the film, responsible for overseeing all aspects of the production, from pre-production to post-production.
- Director of Photography (DP): See Cinematographer.
- Distributor: The company responsible for releasing the film to theaters and other platforms.
- Documentary Filmmaker: Creates non-fiction films, often focusing on real-life events and people.
- Dolly Grip: Operates the dolly, a wheeled platform used to move the camera.
E
- Editor: Assembles the raw footage into the final film, and creates the narrative flow and pacing.
- Electrician: Works with the gaffer to set up and maintain lighting equipment.
- Executive Producer: Often involved in financing and high-level decision-making, but may not be involved in the day-to-day production.
F
- Film Critic: Reviews and analyzes films.
- Film Festival Programmer: Select films to be screened at film festivals.
- Focus Puller: Maintains the camera's focus during filming.
- Foley Artist: Creates and records everyday sound effects for films in post-production.
G
- Gaffer: The head electrician on set, responsible for executing the lighting plan designed by the cinematographer.
- Grip: Responsible for the rigging and support of camera equipment, as well as other on-set tasks.
H
- Hair Stylist: Styles the actors' hair for filming.
K
- Key Grip: The head grip on set, responsible for overseeing the grip crew.
L
- Line Producer: Manages the budget and logistics of a film production.
- Location Manager: Finds and secures locations for filming.
M
- Marketing Manager: Develops and executes the marketing campaign for the film.
- Makeup Artist: Applies makeup to the actors for filming.
- Music Supervisor: Selects and licenses music for the film.
P
- Post-Production Supervisor: Oversees the post-production process, ensures that the film is completed on time and within budget.
- Producer: Oversees the entire film production, from development to distribution. There are various types of producers with different responsibilities.
- Production Assistant (PA): Entry-level position that covers various tasks on set, from running errands to assisting the crew.
- Production Designer: Creates the overall visual look of the film, including sets, costumes, and props.
- Prop Master: Responsible for acquiring and managing all props used in the film.
- Publicist: Promotes the film to the media and the public.
S
- Sales Agent: Sells the film to distributors in different territories.
- Screenwriter: Writes the screenplay.
- Script Supervisor: Maintains continuity during filming so that everything matches from shot to shot.
- Set Decorator: Furnishes and decorates sets, and adds details that create the film's environment.
- Sound Designer: Creates the film's sound effects and ambiance.
- Sound Mixer (Re-recording Mixer): Blends all the different sound elements (dialogue, music, sound effects) into the final soundtrack.
- Storyboard Artist: Creates visual representations of scenes in the film, helping the director and cinematographer plan shots.
- Story Editor: Reads and evaluates scripts, providing feedback to writers and producers.
- Stunt Coordinator: Plans and oversees all stunts in the film, ensuring the safety of the performers.
T
- Transportation Coordinator: Manages the transportation of cast, crew, and equipment to and from the set.
V
- Visual Effects (VFX) Artist: Creates visual effects using computer software.
- Visual Effects (VFX) Supervisor: Oversees the visual effects for the film.
Let us know if we missed any definitions in the comments.







![First-Person Psychological Horror Title ‘The Cecil: The Journey Begins’ Arrives on Steam April 3 [Trailer]](https://i0.wp.com/bloody-disgusting.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/cecil.jpg?fit=900%2C580&ssl=1)
























































































![‘It Ends’ Review: The Kids Are Not Alright In Alex Ullom’s Evocative Existential Horror Debut [SXSW]](https://cdn.theplaylist.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/12223138/it-ends-sxsw.jpg)


































































































![Silver Airways Can’t Pay for Planes—So It’s Firing Pilots Instead [Roundup]](https://viewfromthewing.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/silver-airways.jpg?#)

![[FINAL WEEK] Platinum Status And 170,000 Points: IHG’s New $99 Credit Card Offer Worth Getting And Keeping](https://viewfromthewing.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/IMG_3311.jpg?#)
























.jpg?#)



























































































































![[Podcast] Should Brands Get Political? The Risks & Rewards of Taking a Stand with Jeroen Reuven](https://justcreative.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/jeroen-reuven-youtube.png)





































































































